Good practices regarding order, hygiene, and cleanliness have always been essential in the various ways an industry approaches its regular activities.
Although at first it may seem that these types of factors are more important in certain industries, such as the agri-food or pharmaceutical sectors, their role is no less relevant in other production environments, making hygiene a key characteristic for any factory that aims to be competitive.
On this subject, we have previously discussed concepts related to the philosophy of Lean Manufacturing, such as that of Housekeeping and that of 5S. These clearly demonstrate that maintaining certain habits of order and cleanliness in industrial production brings benefits related to higher product quality, greater efficiency in work, and greater risk prevention for human teams, to name the most notable ones.
From now on, we will delve into the fundamentals of industrial hygiene, as well as the essential characteristics of its maintenance in the event of a contagion risk.
According to the definition provided in the Encyclopedia of Occupational Health and Safety, published by the ILO (International Labour Organization):
Industrial hygiene is the science of anticipation, identification, evaluation, and control of risks that originate in or are related to the workplace and that may threaten the health and well-being of workers, also considering their potential impact on neighboring communities and the environment in general.
As we can see, this description places special emphasis on everything related to the health and well-being of workers and their surrounding environment. Therefore, it is such an important aspect that it has even led to the creation of reference organizations to promote and advance it, such as the case of the Spanish Association of Industrial Hygiene.
Industrial hygiene is based on 3 basic stages:
- Identification of potential health hazards in the workplace.
- Evaluation of the hazards we have identified. This will help us understand the actual health risk they pose.
- Prevention and control of risks. Once we are certain about the main risk agents and their significance, we will take the necessary measures to eliminate or reduce them to levels that are manageable.
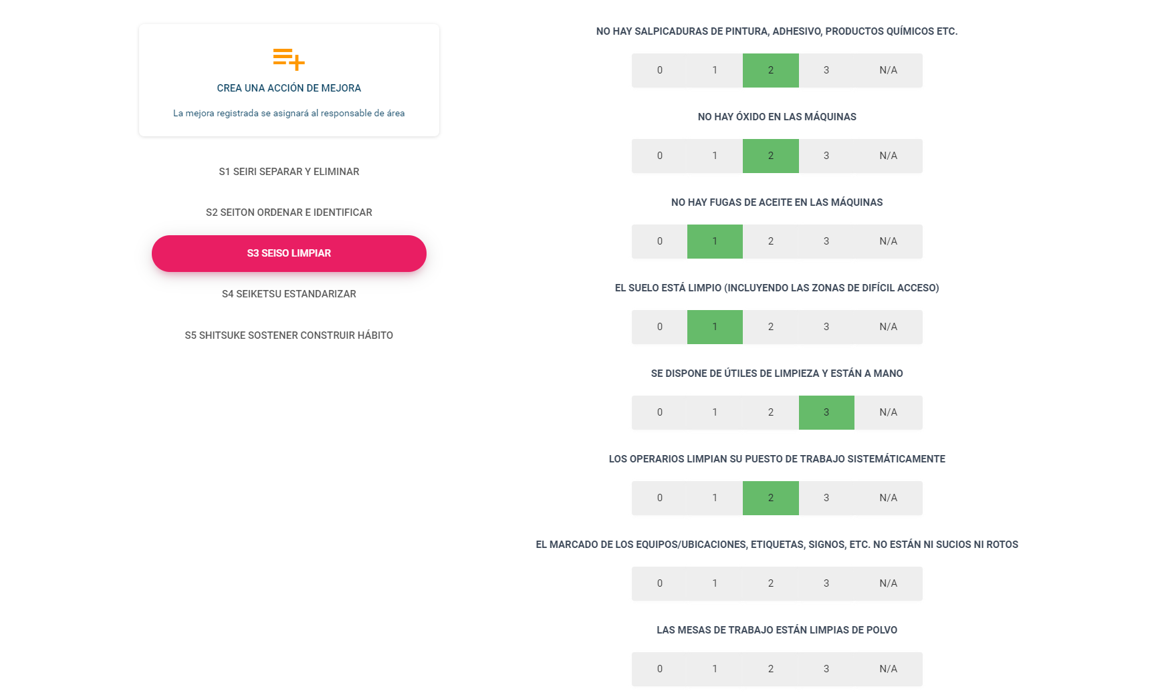
Example of a digital industrial hygiene audit
In cases where the occupational risk of contagion by a pathogenic agent is high, such as the current health situation the entire society is facing, special attention must be paid to certain routines that minimize the spread of the disease.
To help companies and workers be as cautious as possible, the Ministry of Health, together with the Ministry of Labor and Social Economy and the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, has recently published guidelines for good practices in the industrial sector to prevent contagion.
Within this document, we find recommendations on how to act before going to our workplace, during the commute, and how to behave once we are at work. As expected, it is the latter that make up the majority of the publication.
Regarding the measures related to the organization of work, we can highlight:
- Communication and training regarding the detection of symptoms or contact with sick individuals, the risks of the disease, and the protective and preventive measures taken in this regard.
- Delimiting areas to minimize the crossing of people, especially in particularly sensitive places, such as entrances and exits.
- Avoid fingerprint-based timekeeping systems.
- Opt for remote work for workers who are able to do so.
- Establish shifts to avoid high concentrations of people in the facility.
- Organize tasks in a way that ensures the minimum safety distance is maintained at all times.
- Clearly mark the direction of movement within the factory to reduce contact due to the flow of personnel.
- Use common areas in shifts (e.g., dining room, changing room, etc.).
Regarding hygiene itself, recommendations include:
- Carry out cleaning and disinfection actions between the previously established shifts.
- In cases where it is not possible to maintain distance, install elements such as partitions that allow for greater worker isolation without hindering their work.
- Reduce contact with external personnel, such as raw material suppliers, to strictly what is necessary.
- Ventilate the facility regularly.
- Reinforce cleaning in areas with frequent contact, such as door handles, handrails, switches, etc.
- Use individual tools and equipment. If shared, disinfect between uses.
- Provide protective equipment and materials such as soap, hand sanitizer, disposable tissues, etc.
How do audits help?
Having complete control and monitoring of all these variables that affect health at work makes the planning of internal audits necessary. These are even more efficient when accompanied by the appropriate technological tools.
For this reason, we have developed a solution that, first, allows for planning audits by determining the different areas to be analyzed, as well as their responsible parties and dates; furthermore, once the scheduled day arrives, it enables the audit to be carried out thoroughly and impartially; and finally, it provides the necessary mechanisms to analyze the results and facilitate the execution and control of the corrective actions needed for improvement.
In addition, to encourage participation in the continuous monitoring of safety and hygiene at work, a layer of gamification has been added to the process, so that workers are, in a way, rewarded for their collaboration, providing an extra motivation beyond maintaining their safety and health.
It is clear that companies today need to reinforce measures for the protection of their workers, a situation that requires greater control over these measures, which we can achieve through technological solutions like the one we offer at Sixphere.
Do you want to know what we do and how we do it? Visit our success stories and ask us anything you need to know.
KNOWLEDGE / Downloadables
Free eBook
OEE Efficiency

Discover the details of the OEE indicator, how to automate its calculation and the requirements your production processes must meet to implement it.
